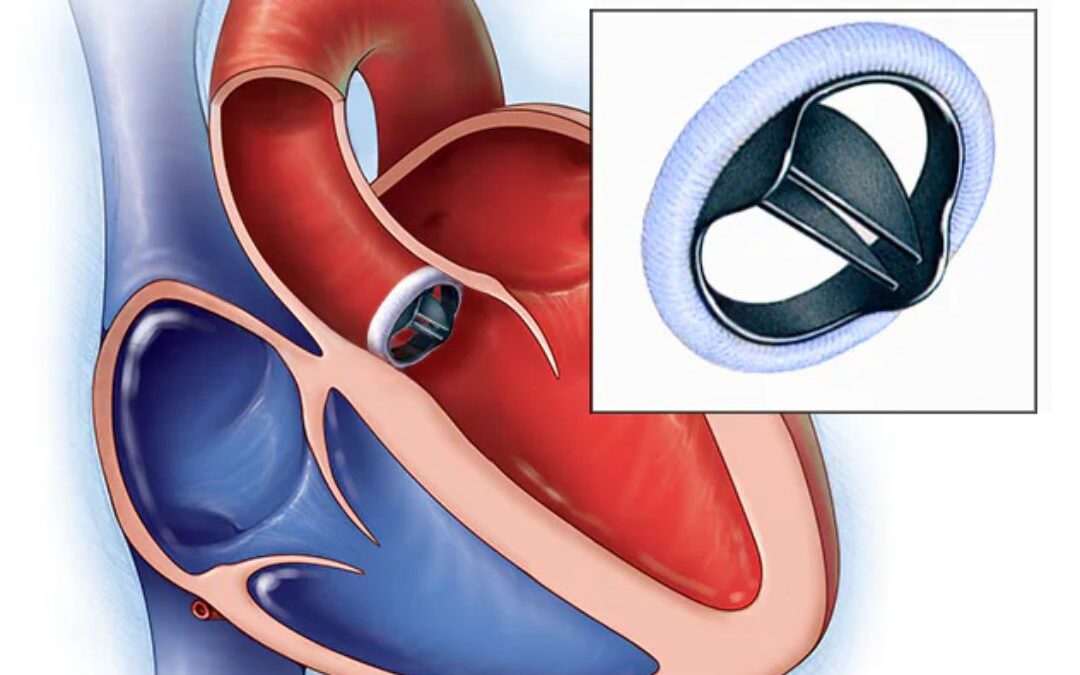
Heart valve disease refers to any condition that affects the valves of the heart. The valves are the flaps of tissue that open and close to allow blood to flow through the heart. There are four valves in the heart: the aortic valve, the mitral valve, the tricuspid valve, and the pulmonary valve. When these valves are damaged or do not work correctly, they can lead to heart valve disease. This can cause a range of symptoms and complications, and it is important to seek medical attention if you suspect that you have heart valve disease.
Signs and Symptoms
The signs and symptoms of heart valve disease can vary depending on the severity of the condition and which valve is affected. Some people may not experience any symptoms at all, while others may experience a range of symptoms that can affect their daily life. Common signs and symptoms of heart valve disease include:
- Shortness of breath, especially during physical activity or when lying down
- Fatigue and weakness
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Dizziness or fainting
- Rapid or irregular heartbeat
- Swelling in the feet, ankles, or abdomen
- Heart palpitations (feeling like your heart is racing or fluttering)
- A cough that does not go away
Complications
If left untreated, heart valve disease can lead to a range of complications, including:
- Heart failure: When the heart cannot pump enough blood to meet the body’s needs.
- Stroke: When blood flow to the brain is blocked or reduced.
- Blood clots: When the blood does not flow smoothly through the heart, blood clots can form, which can cause serious health problems.
- Endocarditis: When the heart valves become infected, which can lead to life-threatening complications.
Treatment Options

The treatment for heart valve disease will depend on the severity of the condition, the valve that is affected, and the symptoms that are present. Treatment options may include:
- Medications: Certain medications can help to control the symptoms of heart valve disease, such as blood thinners to reduce the risk of blood clots, and diuretics to reduce swelling.
- Surgery: In some cases, surgery may be needed to repair or replace the damaged valve. This can be done through open-heart surgery or minimally invasive procedures.
- Catheter-based procedures: Some heart valve procedures can be done using a catheter, which is a thin, flexible tube that is inserted into the body through a small incision.
- Lifestyle changes: Making certain lifestyle changes, such as quitting smoking, eating a healthy diet, and getting regular exercise, can help to manage the symptoms of heart valve disease and reduce the risk of complications.
Conclusion
Heart valve disease is a serious condition that can lead to a range of complications if left untreated. If you are experiencing any of the symptoms of heart valve disease, it is important to seek medical attention right away. Your doctor can perform tests to diagnose the condition and recommend a treatment plan that is right for you. By taking steps to manage heart valve disease, you can reduce your risk of complications and improve your overall health and quality of life.